ลิงค์
http://bss-i.blogspot.com/2015/09/chapter-5-invaders-revenge-interactive.html
วันพุธที่ 30 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2558
Kivy Project : Kivy: Interactive Applications in Python Chapter 4
Improving the User Experience
ใน chapter นี้ จะพูดถึงการนำความรู้ตั้งแต่บทแรก มาใช้
Screen manager – selecting colors for the figures
Screen manager เป็น class ที่ช่วยในการสร้างหน้าจอโปรแกรมอีกจอนึง ซึ่ง screen นี่จะอยู่บน canvas เดี๋ยวกัน มี size เท่ากันกับหน้าต่างวาดรูป โดยในหนังสือจะนำเป็น ColorPicker เป็นหน้าจอที่ใช้สำหรับเลือกสีของตัว Stickman
ขั้นตอนแรกให้ทำการสร้างไฟล์ .kv ไฟล์ขึ้นมา
โค้ดของ comicscreenmanager.kv
# File name: comicscreenmanager.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import FadeTransition kivy.uix.screenmanager.FadeTransition
<ComicScreenManager>:
transition: FadeTransition()
color_picker: _color_picker
ComicCreator:
Screen:
name: 'colorscreen'
ColorPicker:
id: _color_picker
Button:
text: "Select"
pos_hint: {'center_x': .75, 'y': .05}
size_hint: None, None
size: 150, 50
on_press: root.current = 'comicscreen'
จากนั้นให้ไปเปลี่ยน ไฟล์ comiccreator.kv
# File name: comiccreator.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ComicCreator@Screen>:
name: 'comicscreen'
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'left'
anchor_y: 'top'
ToolBox:
id: _tool_box
drawing_space: _drawing_space
comic_creator: root
size_hint: None,None
width: 100
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'right'
anchor_y: 'top'
DrawingSpace:
id: _drawing_space
status_bar: _status_bar
general_options: _general_options
tool_box: _tool_box
size_hint: None,None
width: root.width - _tool_box.width
height: root.height - _general_options.height - _status_bar.height
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'center'
anchor_y: 'bottom'
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'vertical'
GeneralOptions:
id: _general_options
drawing_space: _drawing_space
comic_creator: root
size_hint: 1,None
height: 48
StatusBar:
id: _status_bar
size_hint: 1,None
height: 24
Color Control on the canvas – coloring figures
StencilView – limiting the drawing space
Scatter – multitouching to drag, rotate, and scale
Simple gestures – drawing with the finger
ใน chapter นี้ จะพูดถึงการนำความรู้ตั้งแต่บทแรก มาใช้
Screen manager – selecting colors for the figures
Screen manager เป็น class ที่ช่วยในการสร้างหน้าจอโปรแกรมอีกจอนึง ซึ่ง screen นี่จะอยู่บน canvas เดี๋ยวกัน มี size เท่ากันกับหน้าต่างวาดรูป โดยในหนังสือจะนำเป็น ColorPicker เป็นหน้าจอที่ใช้สำหรับเลือกสีของตัว Stickman
 |
| ColorPicker |
ขั้นตอนแรกให้ทำการสร้างไฟล์ .kv ไฟล์ขึ้นมา
โค้ดของ comicscreenmanager.kv
# File name: comicscreenmanager.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import FadeTransition kivy.uix.screenmanager.FadeTransition
<ComicScreenManager>:
transition: FadeTransition()
color_picker: _color_picker
ComicCreator:
Screen:
name: 'colorscreen'
ColorPicker:
id: _color_picker
Button:
text: "Select"
pos_hint: {'center_x': .75, 'y': .05}
size_hint: None, None
size: 150, 50
on_press: root.current = 'comicscreen'
จากนั้นให้ไปเปลี่ยน ไฟล์ comiccreator.kv
# File name: comiccreator.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ComicCreator@Screen>:
name: 'comicscreen'
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'left'
anchor_y: 'top'
ToolBox:
id: _tool_box
drawing_space: _drawing_space
comic_creator: root
size_hint: None,None
width: 100
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'right'
anchor_y: 'top'
DrawingSpace:
id: _drawing_space
status_bar: _status_bar
general_options: _general_options
tool_box: _tool_box
size_hint: None,None
width: root.width - _tool_box.width
height: root.height - _general_options.height - _status_bar.height
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'center'
anchor_y: 'bottom'
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'vertical'
GeneralOptions:
id: _general_options
drawing_space: _drawing_space
comic_creator: root
size_hint: 1,None
height: 48
StatusBar:
id: _status_bar
size_hint: 1,None
height: 24
StencilView – limiting the drawing space
Scatter – multitouching to drag, rotate, and scale
Simple gestures – drawing with the finger
วันพุธที่ 23 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2558
Kivy Project : Kivy: Interactive Applications in Python Chapter 3
Attributes, id and root
ใน chapter นี้ จะพูดถึง 4 ส่วนประกอบ นี้ เป็นหลัก คือ toolbox, drawing space, general options, and status bar ทั้ง 4 ส่วนประกอบนี้จะมีการโต้ตอบกัน ซึ่งเรามีความจำเป็นต้องเพิ่ม attributes ไปที่ class ของ project สามารถแสดงความสัมพันธ์ในไฟล์ comiccreator ได้ดังนี้
ส่วน comicwidgets.py ให้ดัดแปลงโค้ดดังนี้
# File name: comicwidgets.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
from kivy.graphics import Line
class DraggableWidget(RelativeLayout):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.selected = None
self.touched = False
super(DraggableWidget, self).__init__(**kwargs)
ตรงส่วน __init__ เป็น constructor คลาสนี้จะมี 3 overload method on_touch_down , on_touch_move , on_touch_up
เริ่มที่ on_touch_down
def on_touch_down(self, touch):
if self.collide_point(touch.x, touch.y):
self.touched = True
self.select()
return True
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_down(touch)
ใช้ method colide_point เพื่อเช็คพิกัดของการ touch หรือ คลิก
event ต่อมา
def select(self):
if not self.selected:
self.ix = self.center_x
self.iy = self.center_y
with self.canvas:
self.selected = Line(rectangle=(0,0,self.width,self.height), dash_offset=2)
event นี้คือจะเช็คว่าถ้าคลิิกตรงกลางของ object ต่างๆ จะให้สร้าง กรอบสี่เหลี่มที่เป็นเส้นประล้อมรอบขึ้นมา
ต่อด้วย on_touch_move
def on_touch_move(self, touch):
(x,y) = self.parent.to_parent(touch.x, touch.y)
if self.selected and self.touched and self.parent.collide_point(x - self.width/2, y -self.height/2):
go = self.parent.general_options
go.translation=(touch.x-self.ix,touch.y-self.iy)
return True
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_move(touch)
ตรงส่วนการ drag หรือ การลาก จะมีการเช็ค collide_point ไม่ให้ลาก object ออกไปนอก drawing space ถ้าเงื่อนไขเป็น True ก็จะสั่งให้เรียกใช้ translate method
def translate(self, x, y):
self.center_x = self.ix = self.ix + x
self.center_y = self.iy = self.iy + y
สุดท้าย on_touch_up
def on_touch_up(self, touch):
self.touched = False
if self.selected:
if not self.parent.general_options.group_mode:
self.unselect()
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_up(touch)
on_touch_up event เป็นการคืนค่าสถานะของ on_touch_down ถ้าเช็คแล้วมีการ selected อยู่ ก็จะเรียกใช้ method unselected()
def unselect(self):
if self.selected:
self.canvas.remove(self.selected)
self.selected = None
มีโค้ดอีกนิดหน่อยใน comicwidgets.py
class StickMan(DraggableWidget):
pass
อ้างอิงข้อมูลและรูปภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python
ใน chapter นี้ จะพูดถึง 4 ส่วนประกอบ นี้ เป็นหลัก คือ toolbox, drawing space, general options, and status bar ทั้ง 4 ส่วนประกอบนี้จะมีการโต้ตอบกัน ซึ่งเรามีความจำเป็นต้องเพิ่ม attributes ไปที่ class ของ project สามารถแสดงความสัมพันธ์ในไฟล์ comiccreator ได้ดังนี้
ภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python
การสร้าง ids ด้วยตัวเอง ไม่ควรนำไปใช้ภายนอกภาษา Kivy ควรสร้าง attributes ไว้เรียกใช้ใน Python Code
จากโค้ด comiccreator.kv เรานำมาดัดแปลงดังนี้
# File name: comiccreator.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ComicCreator>:
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'left'
anchor_y: 'top'
ToolBox:
id: _tool_box
drawing_space: _drawing_space
comic_creator: root
size_hint: None,None
width: 100
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'right'
anchor_y: 'top'
DrawingSpace:
id: _drawing_space
status_bar: _status_bar
general_options: _general_options
tool_box: _tool_box
size_hint: None,None
width: root.width - _tool_box.width
height: root.height - _general_options.height - _status_bar.height
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'center'
anchor_y: 'bottom'
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'vertical'
GeneralOptions:
id: _general_options
drawing_space: _drawing_space
comic_creator: root
size_hint: 1,None
height: 48
StatusBar:
id: _status_bar
size_hint: 1,None
height: 24
IDs ที่ highlight ด้วยสีเหลือง คือการประกาศตัวแปร ส่วนที่ hightlight ด้วยสีฟ้า คือการใช้ ids สร้าง attributes มีความสัมพันธ์ดัง comiccreator diagram ก่อนหน้านี้
ชื่อของ attributes ไม่จำเป็นต้องเปลี่ยนแปลงมาก แค่เพิ่ม _ข้างหน้า ก็พอ เช่น _status_bar
Basic widget events – dragging the stickman
ตัวอย่าง basic widget events
mouse event , finger event , pen event
ตัวอย่าง event 3 แบบ
on_touch_down : เมื่อกดคลิกบนหน้าจอ หรือ ทัชบนหน้าจอโปรแกรม
on_touch_move : เมื่อกดคลิกแล้วย้าย เช่น ลากเมาส์
on_touch_up : เมื่อปล่อยเมาส์ หรือ เอานิ้วออกจากหน้าจอ
on_touch_down กับ on_touch_up จะไม่ค่อยมีปัญหาในการแสดงผล แต่ on_touch_move จะไม่แสดงผลที่ไม่มี dragging action วิธีการ add ความสามารถในการ drag สามารถทำได้โดย ดัดแปลงโค้ดดังนี้
โค้ด comicwidgets.kv (add drag capability)
# File name: comicwidgets.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import comicwidgets comicwidgets
<DraggableWidget>:
size_hint: None, None
<StickMan>:
size: 48,48
...
ส่วน comicwidgets.py ให้ดัดแปลงโค้ดดังนี้
# File name: comicwidgets.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
from kivy.graphics import Line
class DraggableWidget(RelativeLayout):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.selected = None
self.touched = False
super(DraggableWidget, self).__init__(**kwargs)
ตรงส่วน __init__ เป็น constructor คลาสนี้จะมี 3 overload method on_touch_down , on_touch_move , on_touch_up
เริ่มที่ on_touch_down
def on_touch_down(self, touch):
if self.collide_point(touch.x, touch.y):
self.touched = True
self.select()
return True
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_down(touch)
ใช้ method colide_point เพื่อเช็คพิกัดของการ touch หรือ คลิก
event ต่อมา
def select(self):
if not self.selected:
self.ix = self.center_x
self.iy = self.center_y
with self.canvas:
self.selected = Line(rectangle=(0,0,self.width,self.height), dash_offset=2)
event นี้คือจะเช็คว่าถ้าคลิิกตรงกลางของ object ต่างๆ จะให้สร้าง กรอบสี่เหลี่มที่เป็นเส้นประล้อมรอบขึ้นมา
 |
| ภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python |
ต่อด้วย on_touch_move
def on_touch_move(self, touch):
(x,y) = self.parent.to_parent(touch.x, touch.y)
if self.selected and self.touched and self.parent.collide_point(x - self.width/2, y -self.height/2):
go = self.parent.general_options
go.translation=(touch.x-self.ix,touch.y-self.iy)
return True
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_move(touch)
ตรงส่วนการ drag หรือ การลาก จะมีการเช็ค collide_point ไม่ให้ลาก object ออกไปนอก drawing space ถ้าเงื่อนไขเป็น True ก็จะสั่งให้เรียกใช้ translate method
def translate(self, x, y):
self.center_x = self.ix = self.ix + x
self.center_y = self.iy = self.iy + y
สุดท้าย on_touch_up
def on_touch_up(self, touch):
self.touched = False
if self.selected:
if not self.parent.general_options.group_mode:
self.unselect()
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_up(touch)
on_touch_up event เป็นการคืนค่าสถานะของ on_touch_down ถ้าเช็คแล้วมีการ selected อยู่ ก็จะเรียกใช้ method unselected()
def unselect(self):
if self.selected:
self.canvas.remove(self.selected)
self.selected = None
มีโค้ดอีกนิดหน่อยใน comicwidgets.py
class StickMan(DraggableWidget):
pass
Localizing coordinates – adding stickmen
หัวข้อนี้จะพูดถึงการทำปุ่มตรงส่วน toolbox ให้มี event
# File name: toolbox.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
import math
from kivy.uix.togglebutton import ToggleButton
from kivy.graphics import Line
from comicwidgets import StickMan, DraggableWidget
class ToolButton(ToggleButton):
def on_touch_down(self, touch):
ds = self.parent.drawing_space
if self.state == 'down' and ds.collide_point(touch.x, touch.y):
(x,y) = ds.to_widget(touch.x, touch.y)
self.draw(ds, x, y)
return True
return super(ToolButton, self).on_touch_down(touch)
def draw(self, ds, x, y):
pass
บรรทัดที่ highlight คือ ส่วนที่ใช้ในการเรียก method ในการวาด ToolStickMan , ToolCircle , และ ToolLine
ตัวอย่างเช่น ToolStickMan เป็น method ในการวาด stickman ขนาด 48x48 pixel บนหน้า drawingspace
class ToolStickman(ToolButton):
def draw(self, ds, x, y):
sm = StickMan(width=48, height=48)
sm.center = (x,y)
ds.add_widget(sm)
Binding and unbinding events – sizing limbs and heads
หัวข้อนี้จะพูดถึงการ ย่อขยายต่างๆ เช่น วงกลม กับ เส้น เพื่อสร้าง stickman ในขนาดที่แตกต่างออกไป
class toolfigure จะมีทั้งหมด 6 medthod
class ToolFigure(ToolButton):
def draw(self, ds, x, y):
(self.ix, self.iy) = (x,y)
with ds.canvas:
self.figure=self.create_figure(x,y,x+1,y+1)
ds.bind(on_touch_move=self.update_figure)
ds.bind(on_touch_up=self.end_figure)
def update_figure(self, ds, touch):
if ds.collide_point(touch.x, touch.y):
(x,y) = ds.to_widget(touch.x, touch.y)
ds.canvas.remove(self.figure)
with ds.canvas:
self.figure = self.create_figure(self.ix, self.iy,x,y)
def end_figure(self, ds, touch):
ds.unbind(on_touch_move=self.update_figure)
ds.unbind(on_touch_up=self.end_figure)
ds.canvas.remove(self.figure)
(fx,fy) = ds.to_widget(touch.x, touch.y)
self.widgetize(ds,self.ix,self.iy,fx,fy)
def widgetize(self,ds,ix,iy,fx,fy):
widget = self.create_widget(ix,iy,fx,fy)
(ix,iy) = widget.to_local(ix,iy,relative=True)
(fx,fy) = widget.to_local(fx,fy,relative=True)
widget.canvas.add(self.create_figure(ix,iy,fx,fy))
ds.add_widget(widget)
def create_figure(self,ix,iy,fx,fy):
pass
def create_widget(self,ix,iy,fx,fy):
pass
class toolfigure จะมีทั้งหมด 6 medthod
- draw: ให้เริ่มวาดจากจุดที่เราคลิกครั้งแรก เช่น เริ่มจากตรงกลางของวงกลม หรือ จุดปลายของเส้น
- update_figure : update จุดเริ่มต้นถึงจุดสุดท้ายของรูป เช่น รัศมีจากจุดกึ่งกลาง หรือ จากจุดหนึ่งไปยังอีกจุดหนึ่งของเส้น
- end_figure : จะบอกจุดสุดท้าย การทำงานคล้ายกับ update_figure
- widgetize : สร้างการ drag figure
- create_figure : เป็น method ที่เรียกใช้ ToolLine ,ToolCircle ในการวาดรูป
- create_widget : ทำงานเหมือน create_figure
ไม่ต้องการให้ on_touch_move กับ on_touch_up events ทำงานตลอดเวลา จึงใช้ Binding and unbinding events ในการแก้ปัญหา (ให้แค่ลากแล้วปล่อย)
โค้ดในส่วนของ class ToolLine ,ToolCircle
class ToolLine(ToolFigure):
def create_figure(self,ix,iy,fx,fy):
return Line(points=[ix, iy, fx, fy])
def create_widget(self,ix,iy,fx,fy):
pos = (min(ix, fx), min(iy, fy))
size = (abs(fx-ix), abs(fy-iy))
return DraggableWidget(pos = pos, size = size)
class ToolCircle(ToolFigure):
def create_figure(self,ix,iy,fx,fy):
return Line(circle=[ix,iy,math.hypot(ix-fx,iy-fy)])
def create_widget(self,ix,iy,fx,fy):
r = math.hypot(ix-fx, iy-fy)
pos = (ix-r, iy-r)
size = (2*r, 2*r)
return DraggableWidget(pos = pos, size = size)
ทั้ง 2 class จะใช้การคำนวณแบบธรรมดาในการกำหนดขนาด
โค้ดในส่วนของ toolbox.kv (มีการแก้ไข)
# File name: toolbox.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import toolbox toolbox
<ToolButton>:
size_hint: None,None
size: 48,48
group: 'tool'
canvas:
PushMatrix:
Translate:
xy: self.x,self.y
canvas.after:
PopMatrix:
<ToolBox@GridLayout>:
cols: 2
padding: 2
tool_circle: _tool_circle
tool_line: _tool_line
tool_stickman: _tool_stickman
ToolCircle:
id: _tool_circle
canvas:
Line:
circle: 24,24,14
ToolLine:
id: _tool_line
canvas:
Line:
points: 10,10,38,38
ToolStickman:
id: _tool_stickman
StickMan:
pos_hint: {'center_x':.5,'center_y':.5}
โค้ดนี้จะมีการเพิ่ม class ที่เราทำใหม่เข้ามา ToolCircle , ToolLine , ToolStickman และมีการเพิ่ม attributes ที่เอาไว้ใช้ในการสร้าง gestures ใน chapter ที่ 4
Binding events in the Kivy language
ในหัวข้อนี้จะพูดถึงการทำ event ในส่วนของ general option
โค้ด generaloption.kv
# File name: generaloptions.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import generaloptions generaloptions
<GeneralOptions>:
orientation: 'horizontal'
padding: 2
Button:
text: 'Clear'
on_press: root.clear(*args)
Button:
text: 'Remove'
on_release: root.remove(*args)
ToggleButton:
text: 'Group'
on_state: root.group(*args)
Button:
text: 'Color'
on_press: root.color(*args)
ToggleButton:
text: 'Gestures'
on_state: root.gestures(*args)
Button หรือ ปุ่มกด จะมี event หลักๆอยู่ 2 อย่างคือ on_press กับ on_release
on_press จะใช้กับ Clear Button กับ Color Button ก็คือกดครั้งเดียวพอ ทำงานเสร็จก็จบ
on_release จะใช้กับ Remove Button กดแล้วสามารถกดต่อได้อีก
on_state จะใช้ ToggleButton ก็คือ กดครั้งนึงไว้แล้วจะทำงานตลอดจนกว่าจะกดอีกครั้งเพื่อหยุด ใช้กับ GroupButton กับ GestureButton
โค้ดในส่วน generaloptions.py
# File name: generaloptions.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout
from kivy.properties import NumericProperty, ListProperty
class GeneralOptions(BoxLayout):
group_mode = False
translation = ListProperty(None)
def clear(self, instance):
self.drawing_space.clear_widgets()
def remove(self, instance):
ds = self.drawing_space
if len(ds.children) > 0:
ds.remove_widget(ds.children[0])
def group(self, instance, value):
if value == 'down':
self.group_mode = True
else:
self.group_mode = False
self.unselect_all()
def color(self, instance):
pass
def gestures(self, instance, value):
pass
def unselect_all(self):
for child in self.drawing_space.children:
child.unselect()
def on_translation(self,instance,value):
for child in self.drawing_space.children:
if child.selected:
child.translate(*self.translation)
class GeneralOptions มีทั้งหมด 7 methods
# File name: generaloptions.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout
from kivy.properties import NumericProperty, ListProperty
class GeneralOptions(BoxLayout):
group_mode = False
translation = ListProperty(None)
def clear(self, instance):
self.drawing_space.clear_widgets()
def remove(self, instance):
ds = self.drawing_space
if len(ds.children) > 0:
ds.remove_widget(ds.children[0])
def group(self, instance, value):
if value == 'down':
self.group_mode = True
else:
self.group_mode = False
self.unselect_all()
def color(self, instance):
pass
def gestures(self, instance, value):
pass
def unselect_all(self):
for child in self.drawing_space.children:
child.unselect()
def on_translation(self,instance,value):
for child in self.drawing_space.children:
if child.selected:
child.translate(*self.translation)
class GeneralOptions มีทั้งหมด 7 methods
- clear : ล้าง widget ที่เราวาดใน drawing space ทั้งหมด
- remove : ลบการวาดครั้งล่าสุด ถ้ากดอีกก็จะลบการวาดครั้งก่อนหน้านั้นไปเรื่อยๆ
- group : ถ้าคลิกเลือกจะมีการเปลี่ยนโหมด จาก True เป็น False
- color : ในที่นี้ยังไม่มี event
- gesture : ในที่นี้ยังไม่มี event
- unselect_all : ทำงานเมื่อไมได้คลิกรูปใดๆ
- on_translation :
Creating your own events – the magical properties
การสร้าง properties
ตัวอย่าง types of properties
NumericProperty , StringProperty , ListProperty , DictProperty , or ObjectProperty
ถ้าเป็น Kivy property จะให้ตั้งชื่อโดย ใส่ on_ หน้าชื่อของ properties เช่น state property ของ
ToogleButton ก็จะเป็น on_state
นอกจากนี้ยังกล่าวถึงการสร้าง event ของ group ซึ่งใช้ state propertty ของ ToogleButton ซึ่งเราต้องการให้ เมื่อเราอยู่ใน group mode เราสามารถเลือก object หลายๆตัว แล้วลากไปพร้อมๆกันได้
 |
| ภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python |
แก้โค้ดในส่วนของ comicwidgets.py ดังนี้
# File name: comicwidgets.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
from kivy.graphics import Line
class DraggableWidget(RelativeLayout):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.selected = None
self.touched = False
super(DraggableWidget, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def on_touch_down(self, touch):
if self.collide_point(touch.x, touch.y):
self.touched = True
self.select()
return True
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_down(touch)
def select(self):
if not self.selected:
self.ix = self.center_x
self.iy = self.center_y
with self.canvas:
self.selected = Line(rectangle=(0,0,self.width,self.height), dash_offset=2)
def on_touch_move(self, touch):
(x,y) = self.parent.to_parent(touch.x, touch.y)
if self.selected and self.touched and self.parent.collide_point(x - self.width/2, y -self.height/2):
go = self.parent.general_options
go.translation=(touch.x-self.ix,touch.y-self.iy)
return True
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_move(touch)
def translate(self, x, y):
self.center_x = self.ix = self.ix + x
self.center_y = self.iy = self.iy + y
def on_touch_up(self, touch):
self.touched = False
if self.selected:
if not self.parent.general_options.group_mode:
self.unselect()
return super(DraggableWidget, self).on_touch_up(touch)
def unselect(self):
if self.selected:
self.canvas.remove(self.selected)
self.selected = None
class StickMan(DraggableWidget):
pass
Kivy and properties
หัวข้อนี้ก็จะเป็นตัวอย่างของ property ใน Kivy
ตัวอย่างจากโค้ด statusbar.py
# File name: statusbar.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout
from kivy.properties import NumericProperty, ObjectProperty
class StatusBar(BoxLayout):
counter = NumericProperty(0)
previous_counter = 0
def on_counter(self, instance, value):
if value == 0:
self.msg_label.text = "Drawing space cleared"
elif value - 1 == self.__class__.previous_counter:
self.msg_label.text = "Widget added"
elif value + 1 == StatusBar.previous_counter:
self.msg_label.text = "Widget removed"
self.__class__.previous_counter = value
มีการใช้ NumericProperty (on_counter) ในการนับ Figure ที่เราสร้าง
โค้ดในส่วน statusbar.kv
# File name: statusbar.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import statusbar statusbar
<StatusBar>:
msg_label: _msg_label
orientation: 'horizontal'
Label:
text: 'Total Figures: ' + str(root.counter)
Label:
id: _msg_label
text: "Kivy started"
ส่วนต่อมาเราต้องการที่ count หรือนับ figure ที่อยู่บน drawings space ให้ทำการแก้ไขโค้ดใน drawingspace.py ดังนี้
# File name: drawingspace.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
class DrawingSpace(RelativeLayout):
def on_children(self, instance, value):
self.status_bar.counter = len(self.children)
โค้ดในส่วนของ drawingspace.kv
# File name: drawingspace.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
#:import drawingspace drawingspace
<DrawingSpace@RelativeLayout>:
 |
| หน้าต่างเริ่มต้นโปรแกรม |
 |
| ทดลองสร้าง Figure ต่างๆ |
 |
| เมื่อคลิกเมาส์ที่ figure จะมีการสร้าง กรอบสี่เหลี่ยมที่เป็นเส้นประล้อมรอบ |
 |
| ลองกด clear button จะเห็นได้ว่า figure นั้นถูกลบไปหมดแล้ว และมีข้อความแสดง Drawing space cleared |
 |
| ลองสร้าง Stickman แล้วใช้คำสั่ง Group |
 |
| สามารถเคลื่อนย้าย Stickman ได้ |
 |
| ทดลองสร้าง Stickman 2 ตัว |
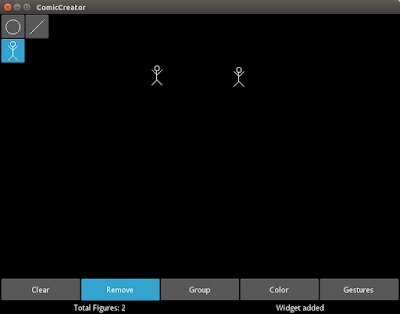 |
| ทดลองใช้คำสั่ง Remove |
 |
| จะเห็นได้ว่าตัวที่เพิ่มเข้ามาล่าสุดถูก Remove ออกไป |
Comic Creator Chapter 2
Comic creator – PushMatrix and PopMatrix
หลังจากที่เราได้สร้าง GUI ไปใน chapter 1 ก็ได้เวลาสร้างตัวละครกันแล้ว
Builder.load_file('comicwidgets.kv')
ในส่วนของ commicwidgets.kv
# File name: comicwidgets.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<StickMan@RelativeLayout>:
size_hint: None, None
size: 48,48
canvas:
PushMatrix
Line:
circle: 24,38,5
Line:
points: 24,33,24,15
Line:
points: 14,5,24,15
Line:
points: 34,5,24,15
Translate:
y: 48-8
Rotate:
angle: 180
axis: 1,0,0
Line:
points: 14,5,24,15
Line:
points: 34,5,24,15
PopMatrix
โค้ดนี้จะพูดถึงการสร้าง stickman โดยถ้าต้องการคืนค่าการวาด stickman ของเรา สามารถทำได้โดยใช้ Kivy Instruction 2 ตัวนี้ PushMatrix และ PopMatrix ในตอนแรก เรา PushMatrix มันจะเก็บค่า state ปัจจุบันเอาไว้ จนกว่าเราจะปิดโปรแกรมหรือทำอย่างอื่น หากเราต้องการคืนค่าไป state ก่อนหน้านี้ ให้คลิกที่เดิมอีกที จะเป็นการคืนค่า state เราเรียกว่า PopMatrix
ต่อมาเราทำการเพิ่มรูปร่างให้กับ ToolButton (วงกลม กับ เส้นตรง) ใน ToolBox ททางด้านซ้ายบน ทำการแก้โค้ด toolbox.kv ดังนี้
# File name: toolbox.kv
<ToolButton@ToggleButton>:
size_hint: None,None
size: 48,48
group: 'tool'
canvas:
PushMatrix:
Translate:
xy: self.x,self.y
canvas.after:
PopMatrix:
<ToolBox@GridLayout>:
cols: 2
padding: 2
ToolButton:
canvas:
Line:
circle: 24,24,14
ToolButton:
canvas:
Line:
points: 10,10,38,38
ToolButton:
StickMan:
pos_hint: {'center_x':.5,'center_y':.5}
ทำการเพิ่มโค้ดในส่วนของ drawingspace.kv
# File name: drawingspace.kv
<DrawingSpace@RelativeLayout>:
StickMan:
pos_hint: {'center_x':.5,'center_y':.5}
canvas.before:
Translate:
xy: -self.width/2, -self.height/2
Scale:
xyz: 2,2,0
StickMan:
ผลลัพท์ที่ได้จากการรัน file comiccreator.py
อ้างอิงข้อมูลและรูปภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python
หลังจากที่เราได้สร้าง GUI ไปใน chapter 1 ก็ได้เวลาสร้างตัวละครกันแล้ว
Builder.load_file('comicwidgets.kv')
ในส่วนของ commicwidgets.kv
# File name: comicwidgets.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<StickMan@RelativeLayout>:
size_hint: None, None
size: 48,48
canvas:
PushMatrix
Line:
circle: 24,38,5
Line:
points: 24,33,24,15
Line:
points: 14,5,24,15
Line:
points: 34,5,24,15
Translate:
y: 48-8
Rotate:
angle: 180
axis: 1,0,0
Line:
points: 14,5,24,15
Line:
points: 34,5,24,15
PopMatrix
โค้ดนี้จะพูดถึงการสร้าง stickman โดยถ้าต้องการคืนค่าการวาด stickman ของเรา สามารถทำได้โดยใช้ Kivy Instruction 2 ตัวนี้ PushMatrix และ PopMatrix ในตอนแรก เรา PushMatrix มันจะเก็บค่า state ปัจจุบันเอาไว้ จนกว่าเราจะปิดโปรแกรมหรือทำอย่างอื่น หากเราต้องการคืนค่าไป state ก่อนหน้านี้ ให้คลิกที่เดิมอีกที จะเป็นการคืนค่า state เราเรียกว่า PopMatrix
ต่อมาเราทำการเพิ่มรูปร่างให้กับ ToolButton (วงกลม กับ เส้นตรง) ใน ToolBox ททางด้านซ้ายบน ทำการแก้โค้ด toolbox.kv ดังนี้
# File name: toolbox.kv
<ToolButton@ToggleButton>:
size_hint: None,None
size: 48,48
group: 'tool'
canvas:
PushMatrix:
Translate:
xy: self.x,self.y
canvas.after:
PopMatrix:
<ToolBox@GridLayout>:
cols: 2
padding: 2
ToolButton:
canvas:
Line:
circle: 24,24,14
ToolButton:
canvas:
Line:
points: 10,10,38,38
ToolButton:
StickMan:
pos_hint: {'center_x':.5,'center_y':.5}
ทำการเพิ่มโค้ดในส่วนของ drawingspace.kv
# File name: drawingspace.kv
<DrawingSpace@RelativeLayout>:
StickMan:
pos_hint: {'center_x':.5,'center_y':.5}
canvas.before:
Translate:
xy: -self.width/2, -self.height/2
Scale:
xyz: 2,2,0
StickMan:
ผลลัพท์ที่ได้จากการรัน file comiccreator.py
อ้างอิงข้อมูลและรูปภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python
Comic Creator Chapter 1
ตัวอย่างการทำ Application Comic Creator
ขั้นตอนแรกของการทำ App เราควรร่างแบบ GUI ไว้ในกระดาษก่อน กำหนดว่าส่วนไหนจะให้ทำอะไร อยู่ตรงไหนของหน้าต่าง App
กำหนดส่วนประกอบต่างๆ ของ App ด้วย Layout ที่เรียนมาในบทที่ 1 ดังนี้
หลังจากที่เราได้กำหนดส่วนต่างแล้ว ก็ทำการสร้างไฟล์ของพื้นที่ส่วนต่างขึ้นมา comiccreator.
py , comiccreator.kv , toolbox.kv , generaltools.kv , drawingspace.kv , และ
statusbar.kv
โค้ดในส่วนของ commiccreator.py
# File name: comiccreator.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.lang import Builder
from kivy.uix.anchorlayout import AnchorLayout
Builder.load_file('toolbox.kv')
Builder.load_file('drawingspace.kv')
Builder.load_file('generaloptions.kv')
Builder.load_file('statusbar.kv')
class ComicCreator(AnchorLayout):
pass
class ComicCreatorApp(App):
def build(self):
return ComicCreator()
if __name__=="__main__":
ComicCreatorApp().run()
Builder.load_file('....') คือการโหลดไฟล์ ซึ่งจะเห็นได้ว่าไม่จำเป็นต้องโหลดไฟล์ commiccreator.kv เนื่องจากไฟล์นี้จะถูกโหลดโดยอัตโนมัติจากการเรียกใช้ ComicCreatorApp
สำหรับ Comiccreator เราเลือกใช้ AnchorLayout ซึ่งไม่ใช่ทางเลือกเดียว แต่ว่าถ้าถึงขั้นตอนในการเขียน code ขั้นต่อไปจะสามารถทำได้ดีกว่า
โค้ดในส่วนของ commiccreator.kv
# File name: comiccreator.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ComicCreator>:
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'left'
anchor_y: 'top'
ToolBox:
id: _tool_box
size_hint: None,None
width: 100
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'right'
anchor_y: 'top'
DrawingSpace:
size_hint: None,None
width: root.width - _tool_box.width
height: root.height - _general_options.height - _status_bar.height
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'center'
anchor_y: 'bottom'
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'vertical'
GeneralOptions:
id: _general_options
size_hint: 1,None
height: 48
StatusBar:
id: _status_bar
size_hint: 1,None
height: 24
สร้าง ToolButton กำหนดขนาดโดย drawing tools และใช้ Kivy Widget : ToolgleButton
สิ่งที่แตกต่างจาก button ปกติก็คือ มันจะคลิกใช้ไปเรื่อยๆจนกว่าเราจะกดคลิกที่ตัวมันอีกที ตัวอย่าง
โค้ดในส่วนของ toolbox.kv
# File name: toolbox.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ToolButton@ToggleButton>:
size_hint: None,None
size: 48,48
group: 'tool' #คำสั่งรวมกลุ่ม button
<ToolBox@GridLayout>:
cols: 2
padding: 2
ToolButton:
text: 'O'
ToolButton:
text: '/'
ToolButton:
text: '?'
โค้ดในส่วนของ generaloptions.kv
# File name: generaloptions.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<GeneralOptions@BoxLayout>:
orientation: 'horizontal'
padding: 2
Button:
text: 'Clear'
Button:
text: 'Remove'
ToggleButton:
text: 'Group'
Button:
text: 'Color'
ToggleButton:
text: 'Gestures'
ตรงส่วนนี้เราไม่ต้องการให้ button อยู่ใน group เดียวกัน เนื่องจาก button แต่ละอันไม่ได้มีการทำงานที่เกี่ยวข้องกัน ในโค้ดนี้จะยังไม่มีการทำงานใดๆเมื่อกดปุ่ม เป็นเพียงแค่ส่วนของ interface เท่านั้น
โค้ดในส่วนของ statusbar.kv
# File name: statusbar.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<StatusBar@BoxLayout>:
orientation: 'horizontal'
Label:
text: 'Total Figures: ?'
Label:
text: "Kivy started"
ผลที่ได้จากการใช้ BoxLayout ก็คือตรงส่วนที่เป็น buttons จะเป็น labels แทน
โค้ดในส่วนของ drawingspace.kv
# File name: drawingspace.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<DrawingSpace@RelativeLayout>:
Label:
markup: True
text: "[size=32px][color=#3e6643]The[/color] [sub]Comic[/sub] [i][b]Creator[/b][/i][/size]"
DrawingSpace เป็น subclass ของ RelativeLayout แนะนำให้ใช้ Kivy markup ซึ่งเป็น feature ในการออกแบบ Label class การทำงานของมันจะคล้ายๆกับ XML based languages
เมื่อทำการรันไฟล์ commiccreator.py จะได้หน้าตา GUI ออกมาเป็นแบบนี้ ซึ่งนี่เป็นเพียง GUI เท่านั้น ยังไม่มีการทำงานใดๆ
อ้างอิงข้อมูลและรูปภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python
 |
| ตัวอย่างการออกแบบ GUIภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python |
- ใช้ AnchorLayout สำหรับ toolbox area ตรงส่วน มุมซ้ายบน
- ใช้ Gridlayout สำหรับ drawing tools 2 columns
- ใช้ AnchorLayout สำหรับ drawing space ตรงส่วน มุมขวาบน
- ใช้ RelativeLayout สำหรับ พื้นที่ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการวาด
- ใช้ AnchorLayout สำหรับ general options และ status bar ตรงส่วนล่าง
- ใช้ BoxLayout ในแนวตั้งเพื่อจัดตำแหน่งของ general option ที่ด้านบนของ status bar และ ใช้ BoxLayout ในแนวนอนสำหรับ ปุุ่มกดของ general option และ label ของ status bar
หลังจากที่เราได้กำหนดส่วนต่างแล้ว ก็ทำการสร้างไฟล์ของพื้นที่ส่วนต่างขึ้นมา comiccreator.
py , comiccreator.kv , toolbox.kv , generaltools.kv , drawingspace.kv , และ
statusbar.kv
โค้ดในส่วนของ commiccreator.py
# File name: comiccreator.py
import kivy
kivy.require('1.7.0')
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.lang import Builder
from kivy.uix.anchorlayout import AnchorLayout
Builder.load_file('toolbox.kv')
Builder.load_file('drawingspace.kv')
Builder.load_file('generaloptions.kv')
Builder.load_file('statusbar.kv')
class ComicCreator(AnchorLayout):
pass
class ComicCreatorApp(App):
def build(self):
return ComicCreator()
if __name__=="__main__":
ComicCreatorApp().run()
Builder.load_file('....') คือการโหลดไฟล์ ซึ่งจะเห็นได้ว่าไม่จำเป็นต้องโหลดไฟล์ commiccreator.kv เนื่องจากไฟล์นี้จะถูกโหลดโดยอัตโนมัติจากการเรียกใช้ ComicCreatorApp
สำหรับ Comiccreator เราเลือกใช้ AnchorLayout ซึ่งไม่ใช่ทางเลือกเดียว แต่ว่าถ้าถึงขั้นตอนในการเขียน code ขั้นต่อไปจะสามารถทำได้ดีกว่า
โค้ดในส่วนของ commiccreator.kv
# File name: comiccreator.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ComicCreator>:
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'left'
anchor_y: 'top'
ToolBox:
id: _tool_box
size_hint: None,None
width: 100
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'right'
anchor_y: 'top'
DrawingSpace:
size_hint: None,None
width: root.width - _tool_box.width
height: root.height - _general_options.height - _status_bar.height
AnchorLayout:
anchor_x: 'center'
anchor_y: 'bottom'
BoxLayout:
orientation: 'vertical'
GeneralOptions:
id: _general_options
size_hint: 1,None
height: 48
StatusBar:
id: _status_bar
size_hint: 1,None
height: 24
สิ่งที่แตกต่างจาก button ปกติก็คือ มันจะคลิกใช้ไปเรื่อยๆจนกว่าเราจะกดคลิกที่ตัวมันอีกที ตัวอย่าง
 |
| Toolbox area with an active ToggleButton |
โค้ดในส่วนของ toolbox.kv
# File name: toolbox.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<ToolButton@ToggleButton>:
size_hint: None,None
size: 48,48
group: 'tool' #คำสั่งรวมกลุ่ม button
<ToolBox@GridLayout>:
cols: 2
padding: 2
ToolButton:
text: 'O'
ToolButton:
text: '/'
ToolButton:
text: '?'
โค้ดในส่วนของ generaloptions.kv
# File name: generaloptions.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<GeneralOptions@BoxLayout>:
orientation: 'horizontal'
padding: 2
Button:
text: 'Clear'
Button:
text: 'Remove'
ToggleButton:
text: 'Group'
Button:
text: 'Color'
ToggleButton:
text: 'Gestures'
ตรงส่วนนี้เราไม่ต้องการให้ button อยู่ใน group เดียวกัน เนื่องจาก button แต่ละอันไม่ได้มีการทำงานที่เกี่ยวข้องกัน ในโค้ดนี้จะยังไม่มีการทำงานใดๆเมื่อกดปุ่ม เป็นเพียงแค่ส่วนของ interface เท่านั้น
| General Option area |
# File name: statusbar.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<StatusBar@BoxLayout>:
orientation: 'horizontal'
Label:
text: 'Total Figures: ?'
Label:
text: "Kivy started"
ผลที่ได้จากการใช้ BoxLayout ก็คือตรงส่วนที่เป็น buttons จะเป็น labels แทน
| Status Bar area |
โค้ดในส่วนของ drawingspace.kv
# File name: drawingspace.kv
#:kivy 1.7.0
<DrawingSpace@RelativeLayout>:
Label:
markup: True
text: "[size=32px][color=#3e6643]The[/color] [sub]Comic[/sub] [i][b]Creator[/b][/i][/size]"
DrawingSpace เป็น subclass ของ RelativeLayout แนะนำให้ใช้ Kivy markup ซึ่งเป็น feature ในการออกแบบ Label class การทำงานของมันจะคล้ายๆกับ XML based languages
เมื่อทำการรันไฟล์ commiccreator.py จะได้หน้าตา GUI ออกมาเป็นแบบนี้ ซึ่งนี่เป็นเพียง GUI เท่านั้น ยังไม่มีการทำงานใดๆ
อ้างอิงข้อมูลและรูปภาพจากหนังสือ Kivy : Interactive Applications in Python
วันพุธที่ 16 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2558
Kivy Project : Kivy: Interactive Applications in Python Chapter 1
ใน Kivy: Interactive Applications in Python Chapter 1 นั้นจะพูดถึง การสร้าง GUI พื้นฐาน ซึ่งประกอบด้วย widgets และ layouts เป็นหลัก ภายในหนังสือ จะใช้ ภาษา Python สร้าง class เพื่อเรียกใช้ และใช้ ภาษา Kivy ในการเขียน widgets และ layout
2. ตั้งชื่อไฟล์ให้มีชื่อเหมือนกันทั้งไฟล์ .py และ .kv เช่น abc.py , abc.kv ควรระวังเรื่องการตั้งชื่อไม่ให้ไปซ้ำกับ libaries ของ kivy เพราะอาจจะทำให้รันไฟล์ไม่ผ่าน
3. เก็บไฟล์ .py และ .kv ไว้ใน directory เดียวกัน
4. สามารถกำหนด size ของ หน้าต่างสดงผลได้โดย พิม --size=500x250 ต่อชื่อไฟล์ (ทำใน terminal
python comiccreator.py --size=500x250 )
ตัวแปรสำหรับการตั้งค่า size ต่างๆ ใน layout และ widgets (ภายในไฟล์ .kv)
การใช้งาน
1. การ run ไฟล์ จะ run ผ่านไฟล์ .py เปิดโดยใช้โปรแกรมเขียน Python ทั่วไป ซึ่งหากไม่มีไฟล์ .kv ก็จะเป็นเพียง หน้าต่างเปล่าๆ2. ตั้งชื่อไฟล์ให้มีชื่อเหมือนกันทั้งไฟล์ .py และ .kv เช่น abc.py , abc.kv ควรระวังเรื่องการตั้งชื่อไม่ให้ไปซ้ำกับ libaries ของ kivy เพราะอาจจะทำให้รันไฟล์ไม่ผ่าน
3. เก็บไฟล์ .py และ .kv ไว้ใน directory เดียวกัน
4. สามารถกำหนด size ของ หน้าต่างสดงผลได้โดย พิม --size=500x250 ต่อชื่อไฟล์ (ทำใน terminal
python comiccreator.py --size=500x250 )
ตัวแปรสำหรับการตั้งค่า size ต่างๆ ใน layout และ widgets (ภายในไฟล์ .kv)
| Property | Value |
| size_hint | กำหนดเป็น [w,h] ความกว้างกับความสูง มีค่าอยู่ระหว่าง 0 -1 หรือ จะตั้งให้เป็น none |
| size_hint_x | ใช้ระบุค่า width หรือ ความกว้าง ค่าอยู่ระหว่าง 0-1 หรือตั้งให้เป็น none |
| size_hint_y | ใช้ระบุค่า height หรือ ความสูง ค่าอยู่ระหว่าง 0-1 หรือตั้งให้เป็น none |
| pos_hint | มี 2 ตัวกำหนดค่าเป็น axis ค่าแรก (x,center_x , right) ค่าที่ 2 (y,center_y,top) หรือกำหนดค่าตั้งแต่ 0-1 |
| size | เป็นคู่อันดับ [w,h] โดยกำหนดค่าเป็น pixel |
| width | กำหนดค่าตามความกว้าง ของหน้าต่าง |
| height | กำหนดค่าตามความสูง ของหน้าต่าง |
| pos | กำหนดค่าเป็นคู่อันดับ [x,y] ซึ่งมีค่าเดียวกับ ตำแน่ง (x,y) |
| x, right, or center_x |
กำหนดค่าเป็นค่าตายตัว ในแกน x |
| y, top, or center_y |
กำหนดค่าเป็นค่าตายตัว ในแกน y |
Download Code ตัวอย่างจากหนังสือ Kivy: Interactive Applications in Python
Code ตัวอย่างจากหนังสือ Kivy: Interactive Applications in Python
สามารถโหลดได้จากลิงค์นี้
https://www.packtpub.com/books/content/support/14365
สามารถโหลดได้จากลิงค์นี้
https://www.packtpub.com/books/content/support/14365
1. ให้กรอกรายละเอียดต่างๆ ให้เรียบร้อย แล้วคลิกที่ Go
2. code จะถูกส่งไปที่ e-mail ที่เรากรอกรายละเอียดไว้
ตัวอย่างไฟล์
วันจันทร์ที่ 7 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2558
วันพุธที่ 2 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2558
โปรแกรม ภารกิจ (mission) //edit
ในเกมออนไลน์ชนิดหนึ่ง มีภารกิจให้ทำอยู่ N ชนิด ในการทำภารกิจแต่ละภารกิจจะใช้พลังงานในการทำแตกต่างกัน และเมื่อทำเสร็จแล้ว จะได้รับค่าประสบการณ์แตกต่างกัน โดยภารกิจชนิดที่ i จะใช้พลังงาน Ai และเมื่อทำเสร็จแล้วจะได้รับค่าประสบการณ์ Bi คุณสามารถเลือกทำภารกิจกี่อย่างก็ได้ (หรือไม่ทำเลยก็ได้) หลังจากทำภารกิจทั้งหมดเสร็จ คุณจะได้คะแนนเท่ากับค่าประสบการณ์รวมทั้งหมดที่ได้ ลบด้วยสองเท่าของพลังงานรวมทั้งหมดที่ใช้ไป นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจะต้องเสียค่าปรับสำหรับภารกิจที่คุณไม่ได้ทำ โดยคุณจะถูกลบคะแนนเท่ากับกำลังสองของจำนวนภารกิจที่ไม่ได้ทำ คุณต้องการเลือกทำภารกิจเพื่อให้ได้คะแนนรวมมากที่สุดเท่าที่จะทำได้
งานของคุณ
จงเขียนโปรแกรมเพื่อรับพลังงานที่ใช้และค่าประสบการณ์ที่ได้รับจากภารกิจต่างๆ แล้วคำนวณหาคะแนนรวมมากที่สุดที่เป็นไปได้
ข้อมูลนำเข้าบรรทัดแรกระบุจำนวนเต็ม N (1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)
อีก N บรรทัดต่อมา ในบรรทัดที่ i+1 (1 ≤ i ≤ N) ระบุจำนวนเต็ม Ai (1 ≤ Ai ≤ 1,000,000) และ Bi (1 ≤ Bi ≤ 1,000,000) แทนพลังงานที่ใช้และค่าประสบการณ์ที่ได้รับจากภารกิจที่ i
ข้อมูลส่งออกมีบรรทัดเดียว แสดงคะแนนรวมที่มากที่สุดที่เป็นไปได้
ที่มา
การแข่งขัน TUMSO ครั้งที่ 8
โจทย์โดย: สุธี เรืองวิเศษ
งานของคุณ
จงเขียนโปรแกรมเพื่อรับพลังงานที่ใช้และค่าประสบการณ์ที่ได้รับจากภารกิจต่างๆ แล้วคำนวณหาคะแนนรวมมากที่สุดที่เป็นไปได้
ข้อมูลนำเข้าบรรทัดแรกระบุจำนวนเต็ม N (1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)
อีก N บรรทัดต่อมา ในบรรทัดที่ i+1 (1 ≤ i ≤ N) ระบุจำนวนเต็ม Ai (1 ≤ Ai ≤ 1,000,000) และ Bi (1 ≤ Bi ≤ 1,000,000) แทนพลังงานที่ใช้และค่าประสบการณ์ที่ได้รับจากภารกิจที่ i
ข้อมูลส่งออกมีบรรทัดเดียว แสดงคะแนนรวมที่มากที่สุดที่เป็นไปได้
ที่มา
การแข่งขัน TUMSO ครั้งที่ 8
โจทย์โดย: สุธี เรืองวิเศษ
| ตัวอย่างข้อมูลนำเข้า | ตัวอย่างข้อมูลส่งออก |
| 3 3 10 4 10 5 10 | 6 |
| 4 6 10 6 20 8 10 8 20 | 9 |
โค้ด
ที่มา http://www.programming.in.th/task/rev2_problem.php?pid=1117
สมัครสมาชิก:
ความคิดเห็น (Atom)







